What is an Incident Response Plan Template?
An incident response plan template is a systematic approach and structured framework designed to:
- Provide a clear, repeatable process that ensures swift and effective action during a crisis.
- Delineate specific steps for detection, containment, eradication, and recovery tailored to various incidents.
- Establish predefined roles and responsibilities, eliminating confusion and enhancing coordination among team members.
- Mitigates damage and ensures compliance with legal and industry standards.
- Help organizations maintain continuity and safeguard their reputation by taking a proactive stance.
This structured approach enhances the organization's ability to handle incidents and builds a culture of preparedness and resilience.
Importance of an Incident Response Plan
An incident response plan is essential for minimizing the impact of security breaches. Quickly identifying and containing threats helps prevent extensive damage and data loss. Clear protocols ensure team members act decisively, reducing downtime and financial repercussions.
Without a well-defined plan, organizations face chaotic responses, leading to prolonged recovery times and increased vulnerability. Effective incident response plans also help comply with regulatory requirements, avoiding hefty fines and legal complications. By practicing these plans through regular drills, teams can identify weaknesses and improve their response strategies.
Real-world examples, such as the swift containment of the WannaCry ransomware attack by organizations with robust incident response plans, highlight the importance of preparedness. An incident response plan protects sensitive information and preserves customer trust, which is invaluable in today’s digital landscape.
Benefits of a Well-Crafted Incident Response Plan
The benefits of a meticulously designed incident response plan are immediate and far-reaching. Rapid threat detection and containment minimize operational disruptions, ensuring business continuity.
Clear, predefined roles and responsibilities streamline communication, allowing teams to act swiftly and cohesively. This efficiency reduces the financial impact of incidents, potentially saving millions in recovery costs.
Regular updates and drills enhance the plan’s effectiveness, aligning it with evolving threats and technologies. A well-crafted incident response plan also bolsters an organization’s reputation, demonstrating a commitment to security and reliability. This trust can be a significant competitive advantage, attracting and retaining customers.
Legal and regulatory compliance becomes more manageable, reducing the risk of fines and sanctions. In high-stakes environments, such as healthcare and finance, the ability to quickly recover from incidents can be the difference between maintaining operational integrity and facing catastrophic consequences.
Key Components of an Incident Response Plan Template
The components of an incident response plan template provide a comprehensive framework for guiding security teams through the complexities of incident management.
By clearly defining the purpose and scope, outlining potential threat scenarios, assigning specific roles and responsibilities, and detailing the incident response process, the template ensures that all team members understand their tasks and the steps to follow. This organized approach enhances the ability to respond swiftly and effectively, ensuring that incidents are managed with minimal disruption and maximum efficiency.
Purpose and Scope
Incident response plan templates help organizations define the goals and boundaries of their response efforts. They clarify the types of incidents the plan covers, ensuring all team members understand their responsibilities.
The template provides focused direction for the response team by setting clear goals, such as minimizing downtime and protecting sensitive data. This clarity prevents confusion during high-stress situations and enables a more effective response. The scope also includes legal and regulatory requirements, ensuring compliance and reducing the risk of penalties.
Threat Scenarios
Each scenario below requires tailored response strategies, emphasizing the importance of a comprehensive incident response plan. Identifying potential threats ensures preparedness, enabling organizations to mitigate risks effectively and maintain operational resilience:
- Ransomware attacks cripple systems, demanding hefty ransoms.
- Insider threats, whether malicious or accidental, jeopardize sensitive data.
- Phishing schemes deceive employees into revealing confidential information.
- Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks overwhelm networks, causing significant downtime.
- Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs) infiltrate networks, remaining undetected for extended periods while exfiltrating valuable data.
- Natural disasters like floods or earthquakes disrupt operations, necessitating swift recovery actions.
Roles and Responsibilities
Assign specific roles to team members, ensuring clear accountability during incidents:
- Incident commanders oversee the entire response, coordinating efforts and making critical decisions.
- Analysts investigate the breach, identifying its scope and impact. Communication officers manage internal and external communications, keeping stakeholders informed.
- Legal advisors ensure compliance with regulations and handle potential liabilities.
- IT specialists work on containment and eradication, restoring systems to normalcy.
Each role requires precise documentation of responsibilities, enabling swift, organized action. Regular training and simulations ensure team members stay prepared, fostering a proactive incident response culture. Clear delineation of duties minimizes confusion and accelerates recovery.
Incident Response Process
Detecting an incident triggers the response process, starting with immediate containment to prevent further damage. Analysts then assess the breach's severity and scope, gathering crucial data for informed decision-making.
Eradication follows, eliminating malicious elements from affected systems. Recovery efforts restore normal operations, ensuring no residual threats linger. Post-incident analysis identifies vulnerabilities and informs future defenses.
Documentation throughout each phase ensures transparency and accountability. Regularly updating the response process based on lessons learned keeps the plan effective and resilient. Engaging all relevant stakeholders during each step fosters a cohesive, efficient response, minimizing downtime and mitigating impact.
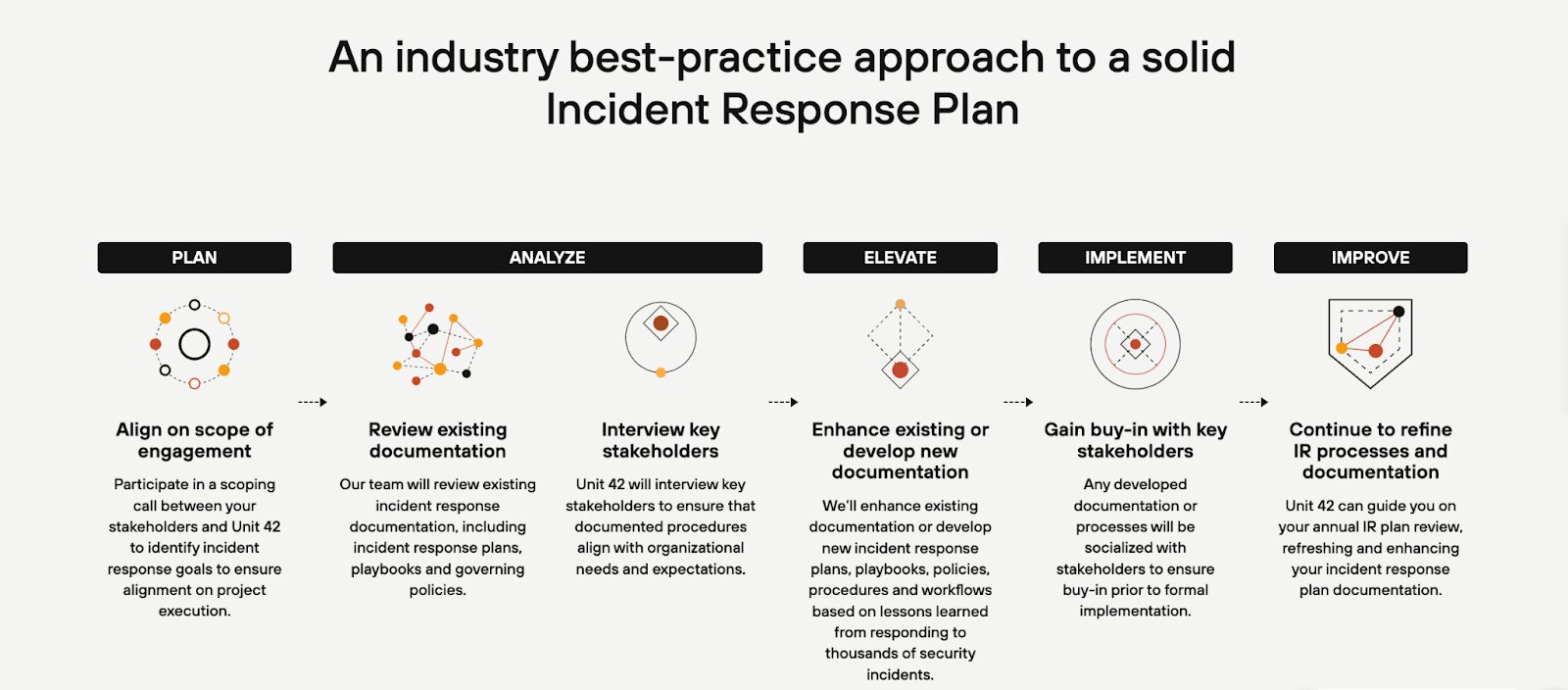
Steps to Create an Incident Response Plan
Creating an incident response plan involves several crucial steps, summarized as:
- Establish a clear policy to guide the response process.
- Assemble a dedicated incident response team with defined roles and responsibilities.
- Develop detailed playbooks for various incident scenarios.
- Craft a communication plan to ensure timely and accurate information flow.
- Regularly test the plan to identify weaknesses.
- Analyze incidents to extract lessons learned.
- Continuously update and refine the plan based on testing outcomes and evolving threats.
This structured approach ensures preparedness and enhances the organization's ability to effectively manage and mitigate security incidents.
Incident Response Plan Templates
Incident response plan templates vary depending on the organization and industry, but here are some examples that can provide a structured approach to handling cybersecurity incidents:
NIST Incident Response Plan Template:
- The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) provides a comprehensive guide for creating an incident response plan, based on their Special Publication 800-61 Revision 2, “Computer Security Incident Handling Guide.”
- Components include preparation, detection and analysis, containment, eradication, and recovery, as well as post-incident activities.
SANS Incident Handler's Handbook:
- The SANS Institute offers the “SANS Incident Handler's Handbook”, a detailed incident response plan template that includes steps for preparation, identification, containment, eradication, recovery, and lessons learned.
- It also includes specific roles and responsibilities, communication plans, and tools needed for effective incident response.
CERT Incident Response Plan:
- The CERT Coordination Center provides the CERT Incident Management, a template for establishing an incident response capability, including policy development, team structure, and incident handling.
- It emphasizes the importance of preparation and provides detailed steps for handling different incidents.
CIS Controls Incident Response Template:
- The Center for Internet Security (CIS) provides the CIS Controls Incident Response Template, which aligns with its CIS Controls framework and emphasizes the importance of establishing and maintaining an incident response capability.
- The template includes specific controls and best practices for incident response.
ISACA Incident Response Plan Template:
- ISACA offers the ISACA Incident Response Plan Template, a comprehensive incident response plan template that includes policy statements, roles and responsibilities, response procedures, and post-incident analysis.
- It is designed to align with industry best practices and regulatory requirements.
These templates can be customized to fit an organization's specific needs and structure, ensuring a robust and effective incident response capability.
Incident Response Plan FAQs
An Incident Response Plan (IRP) is a documented strategy detailing the procedures to follow during a cybersecurity incident. It outlines the roles and responsibilities of the incident response team, the steps for identifying, containing, eradicating, and recovering from an incident, and the methods for preserving evidence and reporting the incident.
The key components of an IRP include:
- Preparation: Developing policies, tools, and resources to handle incidents.
- Identification: Detecting and identifying potential incidents.
- Containment: Limiting the damage and preventing further spread.
- Eradication: Removing the root cause of the incident.
- Recovery: Restoring and validating system functionality.
- Lessons Learned: Analyzing the incident and response to improve future preparedness.
Creating and maintaining an IRP should involve a cross-functional team, including:
- IT and Security Teams: Responsible for technical response and recovery.
- Executive Management: Provides strategic oversight and ensures alignment with business goals.
- Legal and Compliance: Ensures the plan meets regulatory and legal requirements.
- Human Resources: Manages personnel issues and internal communications.
- Public Relations: Handles external communications and media relations.
- Finance: Assesses the financial impact and coordinates resource allocation.
This collaborative approach ensures that the IRP is comprehensive and that all relevant aspects of the organization's operations are considered.